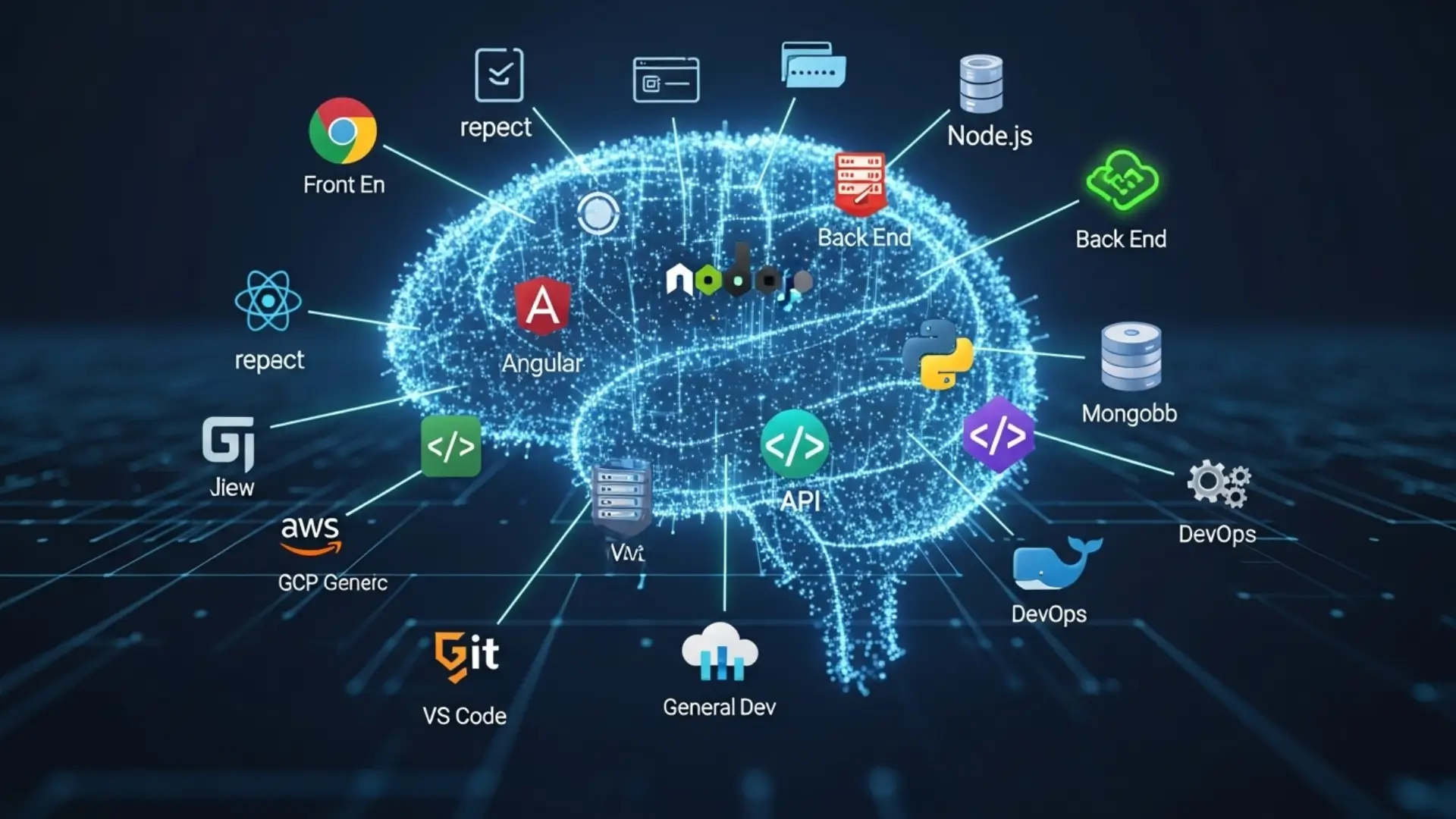
In the fast-paced world of software development, the “full stack developer” stands as a versatile architect, capable of building and maintaining an entire application from the ground up – from the user-facing interface to the underlying database and server logic. This comprehensive role demands a deep understanding of various disciplines and, crucially, a highly optimized toolkit. Without the right set of essential tools and technologies, even the most brilliant full stack developer can find their efficiency plummeting, impacting the delivery of high-quality full stack development services.
This article delves into the indispensable arsenal that empowers modern full stack developers to streamline their workflow, boost productivity, and deliver high-quality solutions with unparalleled efficiency. Whether you’re an aspiring developer eager to build your first end-to-end application or a seasoned pro looking to refine your developer toolkit, understanding these core components is paramount to mastering the full stack development landscape.
The Full Stack Landscape: A Brief Overview
Before diving into specific tools, it’s vital to grasp the breadth of full stack development. It encompasses three primary layers:
- Front-End:The client-side, dealing with everything users see and interact with in their web browser or mobile app. This involves structuring content, styling, and interactivity.
- Back-End:The server-side, responsible for handling business logic, database interactions, authentication, and API communication. This is where the core data processing happens.
- Database:The persistent storage for application data. Choosing the right database is critical for data integrity, retrieval speed, and scalability.
Navigating these interconnected domains requires a diverse skill set and, by extension, a robust full stack developer’s toolkit.

I. Core Development Environments & Editors
At the heart of every developer’s workflow is their chosen Integrated Development Environment (IDE) or code editor. These are more than just text editors; they are sophisticated platforms designed to enhance coding speed, accuracy, and overall developer efficiency.
- Visual Studio Code (VS Code):Arguably the most popular code editor, VS Code offers an incredibly rich ecosystem of extensions, built-in Git integration, intelligent code completion (IntelliSense), and powerful debugging capabilities. It’s lightweight yet feature-packed, making it a favorite for full stack development across various languages.
- IntelliJ IDEA (and its family like WebStorm, PyCharm):For Java, Kotlin, and JavaScript developers, IntelliJ IDEA (or specific variations like WebStorm for front-end) provides an extremely powerful and feature-rich IDE experience. Its advanced refactoring tools, deep code analysis, and robust debugging make it a go-to for complex enterprise-level projects.
- Sublime Text:Known for its speed and minimalism, Sublime Text remains a strong contender for those who prefer a less cluttered interface but still desire powerful features through its plugin architecture.
Why they are essential:These tools offer syntax highlighting, code formatting, integrated terminals, and project management features that dramatically reduce development time and errors, directly contributing to full stack efficiency.
II. Front-End Fundamentals
The user interface is the first impression of any application. Front-end development has evolved rapidly, demanding efficient tools to build dynamic, responsive, and visually appealing experiences.
- Core Languages:
- HTML:The backbone of all web pages, defining content structure.
- CSS:Stylesheets that dictate the visual presentation of HTML. Frameworks like Tailwind CSS or Bootstrap expedite styling.
- JavaScript:The programming language that brings interactivity and dynamic behavior to web pages.
- JavaScript Frameworks & Libraries:These provide pre-built structures and components, significantly accelerating front-end development.
- React:A declarative, component-based JavaScript library for building user interfaces, backed by Facebook. Its virtual DOM ensures highly efficient updates.
- Angular:A comprehensive, opinionated framework maintained by Google, offering a structured approach for large-scale enterprise applications.
- Vue.js:A progressive framework known for its simplicity and flexibility, making it easy to learn and integrate into existing projects.
- State Management Libraries:As applications grow, managing data flow becomes complex. Libraries like Redux (for React), Vuex (for Vue), or simpler alternatives like Zustand or Context API (React) provide predictable state management.
- Build Tools & Bundlers:
- Webpack:A powerful module bundler that takes your code and all its dependencies and bundles them into static assets for the browser.
- Vite:A newer, incredibly fast build tool that offers near-instantaneous hot module replacement (HMR), drastically improving developer productivity during development.
Optimizing Front-End Workflow:Leveraging these frameworks and tools allows full stack developers to create rich UIs efficiently, focusing on user experience rather than reinventing common UI patterns.
III. Back-End Powerhouses
The back-end is the engine of your application, handling data, logic, and server operations. The choice of language and framework here significantly impacts performance, scalability, and back-end development speed. This is often where the initial decision to Choose the Right Tech Stack begins.
- Languages & Runtimes:
- Node.js:A JavaScript runtime environment that allows developers to use JavaScript on the server-side. Its non-blocking, event-driven architecture is ideal for real-time applications and APIs.
- Python:Renowned for its simplicity, readability, and extensive libraries. Popular for web development, data science, machine learning, and automation.
- Java:A robust, mature, and highly scalable language often used for large-scale enterprise applications due to its strong typing and comprehensive ecosystem.
- Go (Golang):Developed by Google, Go is gaining popularity for its concurrency features, performance, and simplicity, making it suitable for high-performance network services.
- Back-End Frameworks:These provide structure and boilerplate for building server-side applications and APIs.
- Express.js (for Node.js):A minimalist and flexible Node.js web application framework that provides a robust set of features for web and mobile applications.
- Django (for Python):A high-level Python web framework that encourages rapid development and clean, pragmatic design. It includes an ORM, admin panel, and more.
- Spring Boot (for Java):Built on top of the Spring framework, Spring Boot simplifies the creation of stand-alone, production-grade Spring-based applications.
- Flask (for Python):A lightweight micro-framework for Python, offering more flexibility than Django for smaller projects or custom setups.
- API Development:
- RESTful APIs:The most common architectural style for web services, using standard HTTP methods for data communication.
- GraphQL:A query language for your API, giving clients the power to ask for exactly what they need and nothing more, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching of data.
Key to Back-End Efficiency:Choosing a framework that aligns with project complexity and team expertise, along with understanding API design principles, is crucial for building maintainable and scalable back-end systems. This foundational choice significantly impacts the entire project’s tech stack.
IV. Database Management
Data is the lifeblood of any application. Database management systems store, retrieve, and organize this data, making their selection and efficient use critical for full stack development.
- Relational Databases (SQL):Structured databases that use tables, rows, and columns, enforced by schemas.
- PostgreSQL:A powerful, open-source object-relational database system known for its robustness, reliability, and rich feature set.
- MySQL:Another popular open-source relational database, widely used for web applications due to its performance and ease of use.
- NoSQL Databases:Non-relational databases that offer more flexible schemas and horizontal scalability.
Database Optimization:Understanding the strengths of each database type and using appropriate indexing, query optimization, and connection pooling techniques are vital for application performance and overall developer efficiency.
V. Version Control & Collaboration
Collaboration is fundamental in modern development.Version control systemsare non-negotiable for managing code changes, tracking history, and facilitating teamwork.
- Git:The undisputed standard for version control. Git allows developers to track every change to their codebase, revert to previous versions, and manage multiple branches of development simultaneously.
- Platforms (Cloud-based Git repositories):
- GitHub:The largest host of source code and development projects, offering powerful collaboration features, issue tracking, and project management.
- GitLab:A comprehensive DevOps platform that provides Git repository management, CI/CD, and more, all in one integrated solution.
- Bitbucket:Popular among teams using Jira for project management, offering integrated private repositories.
Collaboration Best Practices:Mastering Git commands, understanding branching strategies (like Git Flow or GitHub Flow), and leveraging pull requests are essential for efficient team full stack development.
VI. Deployment & DevOps
Moving an application from development to production requires robust deployment strategies and adherence to DevOps principles, which aim to unify development and operations.
- Cloud Platforms:These provide scalable infrastructure and services.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS):The most comprehensive and widely adopted cloud platform, offering a vast array of services for compute, storage, databases, networking, analytics, machine learning, and more.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP):Google’s suite of cloud computing services, known for its strong emphasis on data analytics, machine learning, and Kubernetes.
- Microsoft Azure:Microsoft’s cloud offering, providing a broad range of services, often favored by organizations with existing Microsoft ecosystems.
- Containerization:
- Docker:A platform that uses OS-level virtualization to deliver software in packages called containers. Containers are lightweight, portable, and ensure consistency across different environments.
- Kubernetes:An open-source container orchestration system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Essential for managing complex, microservices-based architectures.
- CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery):Automating the build, test, and deployment process.
- Jenkins:A powerful open-source automation server for building, testing, and deploying software.
- GitLab CI/CD:Built directly into GitLab, offering a seamless CI/CD pipeline integrated with your version control.
- GitHub Actions:Provides flexible CI/CD workflows directly within your GitHub repositories.
DevOps for Efficiency:Implementing CI/CD pipelines and embracing containerization significantly reduces manual errors, speeds up deployments, and ensures consistent environments, leading to massive efficiency gains for full stack developers.
VII. Testing & Debugging
No application is complete without thorough testing. Full stack developers must ensure their code is robust, reliable, and free of bugs.
- Testing Frameworks:
- Jest & React Testing Library (Front-end):Popular for unit and integration testing React components.
- Cypress / Playwright (End-to-End):Tools for testing the entire application flow from a user’s perspective.
- Supertest / Pytest (Back-end):For testing API endpoints and back-end logic.
- Debugging Tools:
- Browser Developer Tools:Essential for front-end debugging (elements, console, network, performance).
- IDE Debuggers:Built into VS Code, IntelliJ IDEA, etc., allowing breakpoint setting, variable inspection, and step-by-step execution.
Quality Assurance:Integrating automated testing into the CI/CD pipeline catches bugs early, saving significant time and effort in the long run and ensuring the stability of the full stack application.
VIII. Productivity & Project Management
Beyond coding, managing tasks, communicating effectively, and organizing the development process are crucial for developer productivity.
- Project Management Tools:
- Jira:A powerful tool for issue tracking and agile project management, widely used by software development teams.
- Trello:A flexible and visual way to manage projects and tasks using Kanban boards.
- Asana:A versatile work management platform for organizing, tracking, and managing team’s work.
- Communication & Collaboration Platforms:
- Slack:A widely used messaging platform for team communication, integrating with many development tools.
- Microsoft Teams:A communication and collaboration platform that combines workplace chat, video meetings, file storage, and application integration.
Workflow Enhancement:Utilizing these tools helps full stack developers stay organized, communicate seamlessly, and manage their time effectively, ultimately contributing to overall project efficiency.
The Evolving Toolkit: Continuous Learning is Key
The world of technology is in constant flux. New frameworks, languages, and tools emerge regularly. A truly effective full stack developer’s toolkit is not static; it evolves. The ability to embrace continuous learning, experiment with new technologies, and adapt to industry trends is perhaps the most important “tool” of all.
Conclusion
Building an efficient full stack developer’s toolkit is an ongoing journey, but the foundations outlined above are critical for any developer aiming for excellence. By strategically selecting and mastering these essential tools and technologies, and always remembering to Choose the Right Tech Stack for each unique project, you can significantly enhance your developer efficiency, streamline your workflow, and build robust, high-quality applications with confidence. From powerful IDEs and cutting-edge front-end frameworks to scalable back-end systems and robust DevOps pipelines, each component plays a vital role in empowering your success.