In today’s competitive online landscape, website performance is more critical than ever for driving user engagement and maintaining search engine rankings. Google’s Core Web Vitals, introduced in 2020, are a set of metrics designed to measure the user experience on a website, including loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability. In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into Core Web Vitals, explore their impact on search rankings, and discuss strategies for improving your site’s performance to stay ahead of the competition.
Understanding Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are comprised of three key metrics:
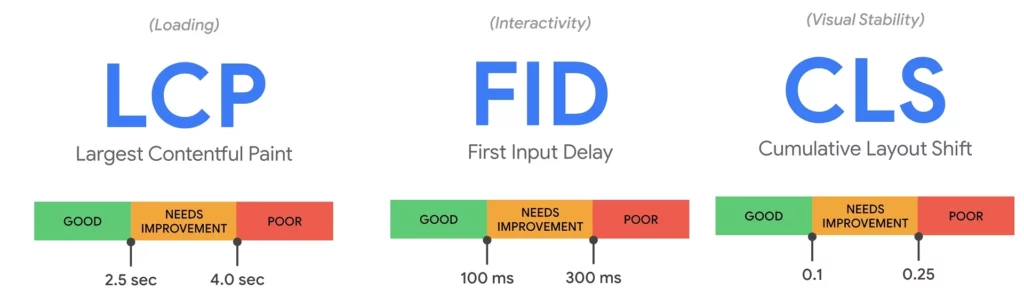
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This metric measures the time it takes for the largest content element on the page to load, reflecting the perceived loading speed for users. A good LCP score is 2.5 seconds or less.
First Input Delay (FID): FID measures the time it takes for a page to become interactive, or the delay between a user’s first interaction with a page and the browser’s response. A good FID score is 100 milliseconds or less.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): CLS quantifies the visual stability of a page by measuring how much elements on the page shift during loading. A good CLS score is 0.1 or lower.
Improving your Core Web Vitals scores can positively impact your site’s user experience and search rankings, as Google now considers these metrics as part of its ranking algorithm.
Strategies to Improve Core Web Vitals
Optimize images and media: Large, unoptimized images can significantly slow down your site’s loading speed, negatively impacting your LCP score. Compress images, use next-gen image formats like WebP, and implement lazy loading techniques to enhance your site’s performance.
Minimize JavaScript and CSS: Excessive JavaScript and CSS can delay page rendering and interactivity, affecting both LCP and FID scores. Minify and compress your code, remove unused scripts, and defer non-critical JavaScript to improve your site’s performance.
Use a content delivery network (CDN): A CDN can help reduce loading times by serving your site’s content from a server closer to the user’s location. This can result in faster LCP and FID scores.
Improve server response times: Optimizing your server’s response times can have a significant impact on LCP and FID. Implement caching, use a high-quality hosting provider, and optimize your database to reduce server delays.
Prevent layout shifts: To reduce layout shifts and improve your CLS score, specify dimensions for images and other elements, avoid inserting content above existing content, and minimize the use of dynamically injected elements.
Monitor your Core Web Vitals: Use tools like Google Search Console, PageSpeed Insights, and Lighthouse to regularly monitor your site’s Core Web Vitals scores and identify areas for improvement.
By implementing these strategies, you can improve your site’s Core Web Vitals scores, enhance the user experience, and ultimately boost your search engine rankings. Stay ahead of the competition by prioritizing performance and optimizing your website for Google’s ever-evolving ranking factors.
Optimize for Mobile Devices
With the increasing prevalence of mobile devices, it’s crucial to ensure your website is mobile-friendly and performs well on a variety of screen sizes. Google’s mobile-first indexing means that the search engine primarily uses the mobile version of a website to determine its rankings. To optimize your site for mobile devices, consider the following tips:
Responsive design: Implement a responsive design to ensure your website adapts to different screen sizes and provides an optimal user experience on various devices.
Touch-friendly elements: Ensure that buttons, links, and other interactive elements are large enough and spaced appropriately for easy tapping on touchscreens.
Optimize for mobile performance: Mobile devices often have slower internet connections and limited processing power compared to desktop computers. To enhance mobile performance, minimize the use of heavy resources, prioritize above-the-fold content, and reduce the impact of third-party scripts.
Test on multiple devices: Regularly test your website on various devices and screen sizes to identify and resolve potential usability issues.
By incorporating mobile optimization into your overall strategy for improving Core Web Vitals, you can further enhance your site’s user experience and boost your search engine rankings.
Conclusion
In today’s digital landscape, providing an excellent user experience is crucial for both retaining users and maintaining high search engine rankings. Core Web Vitals are essential metrics to monitor and optimize, as they directly impact your website’s performance and user experience. By implementing the strategies discussed in this article, such as optimizing images, minimizing JavaScript and CSS, using a CDN, improving server response times, preventing layout shifts, and optimizing for mobile devices, you can significantly enhance your site’s performance and rankings. Stay ahead of the competition by prioritizing your Core Web Vitals and continually adapting to the ever-evolving search engine algorithms.




1 thought on “A Deep Dive into Core Web Vitals: Improving Your Site’s Performance and Rankings”
Comments are closed.